티스토리 뷰
Dual Latent Variable Model for Low-Resource Natural LanguageGeneration in Dialogue Systems
썰팔이 블로그 2019. 8. 2. 17:41Basic information
Q) Bibliography
Tran, Van-Khanh, and Le-Minh Nguyen. "Dual latent variable model for low-resource natural language generation in dialogue systems." arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.04164 (2018).
Q) Link https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.04164.pdf
Q) Cited by https://learning-engineer.tistory.com/9
Motivation
Q) What is the domain this paper is in?
Low-resource NLG in Spoken dialogue systems (SDSs).
i.e., flight reservations (Levin et al., 2000),
buying a tv or a laptop (Wen et al., 2015b),
searching for a hotel or a restaurant (Wen et al., 2015a), and so forth.
Q) What is the desired task?
Filling in the slot of utterances with appropriate values.
Q) Suggest the running example. What is the main point of the task?
Low-resource (10% of the whole training set) works reasonably well with their proposed models.

Q) What are the previous solutions so far?
Domain adaptation and model designing for low-resource training.
Q) What is the limitation of the previous works?
First, despite providing promising results for low-resource setting problems, the methods still need adequate training data at the source domain site. Second, model designing for the low-resource setting has not been well studied in the NLG literature.
Q) What is the objective of this paper? (to review / to prove / to supplement / to show)
To show their model-based domain adaptation works well.
Q) What is the term this work is called (suggest abbreviation, if exists)?
Dual latent variable model (DVAE)
Q) What is the main figure? What is the main point of it?
The figure explains a VNLG (a generator) and a Variational CNN-DCNN as an auxiliary AE model. There are two VAEs and the RNN/CNN utterance encoder (the left-bottom) are shared by both VAEs.

Q) What is the contribution of this paper?
They (i) propose a variational approach for an NLG problem which benefits the generator to not only outperform the previous methods when there is sufficient training data but also perform acceptably well regarding low-resource data;
(ii) present a variational generator that can also adapt faster to a new, unseen domain using a limited amount of in-domain data;
(iii) investigate the effectiveness of the proposed method in different scenarios, including ablation studies, scratch, domain adaptation, and semi-supervised training with a varied proportion of dataset.
Background
Q) What kinds of attempt were there to solve the same problem?
HLSTM (Wen et al., 2015a), SCLSTM (Wen et al., 2015b), or especially RNN Encoder-Decoder models integrating with attention mechanism, such as Enc-Dec (Wen et al., 2016b), and RALSTM (Tran and Nguyen, 2017).
Q) What is the limitation of the previous works?
small training data easily result in worse generation models in the supervised learning methods.
Q) Which paper is the most similar one? Why is that?
This paper solves the same problem (task-oriented dialogue)
Mi, Fei, et al. "Meta-Learning for Low-resource Natural Language Generation in Task-oriented Dialogue Systems." arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.05644 (2019).
Q) What point is the difference between that similar work and this paper?
(Mi, Fei, et al. 2019) is optimization-based, while this paper (Tran and Van-Khanh, et al. 2018) is (latent) model-based.
Model
Q) Which ML model did they use?
baseline RALSTM
C-VNLG (= RALSTM + Variational inference)
DualVAE (= C-VNLG + Variational CNNDCNN)
CrossVAE (= DualVAE + Cross-training)
Q) How many parameters are there?
In this work, the CNN Utterance Encoder consists of L = 3 layers, which for a sentence of length T = 73, embedding size d = 100, stride length s = {2, 2, 2}, number of filters k = {300, 600, 100} with filter sizes h = {5, 5, 16}, results in feature maps $\mathbf{V}$ of sizes {35 × 300, 16 × 600, 1 × 100}, in which the last feature map corresponds to latent representation vector $\mathbf{h_U}$.
Q) How much was the training cost? What facilities did the authors use?
Unknown
Q) Describe the algorithm.
Q) Suggest the main formulation.
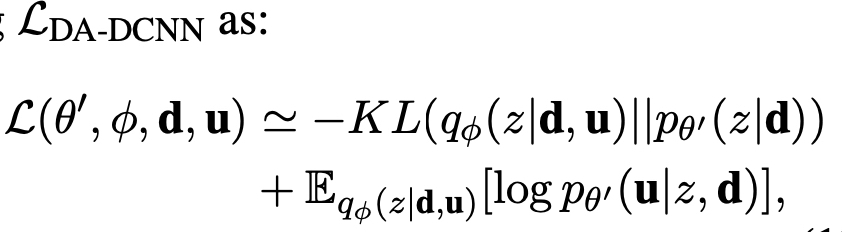

Q) What are the limitations of the model?
Q) Is the code for replication available?
Q) What are the baseline models?
Dataset
Q) Which dataset is used?
Q) How large is the dataset (w.r.t. MB and w.r.t. the number of elements)?
Q) Is the dataset available in public? If yes, where can we get that?
Q) Suggest the sample data?
Results
Q) What kind of metrics did they use?
Q) How good is the result?
Q) Are those metrics reasonable for this work? why is that?
Q) What is the limitation of the results?
Further Questions
Q) Has the algorithm been applied to any (NLP, vision, speech) application?
Q) If so, what are the tasks that the algorithm is applied to learn from?
Q) Is any change to the algorithm needed for the (NLP, vision, speech) application?
Q) Is this the only way to solve the problem?
Q) Is the work applicable to the Question Answering task?
'연구' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 본업 (0) | 2019.09.09 |
|---|---|
| Original papers (0) | 2019.08.03 |
| Meta-Learning for Low-resource Natural Language Generation in Task-oriented Dialogue Systems (0) | 2019.08.02 |
| Questions for understanding a paper (0) | 2019.08.02 |
